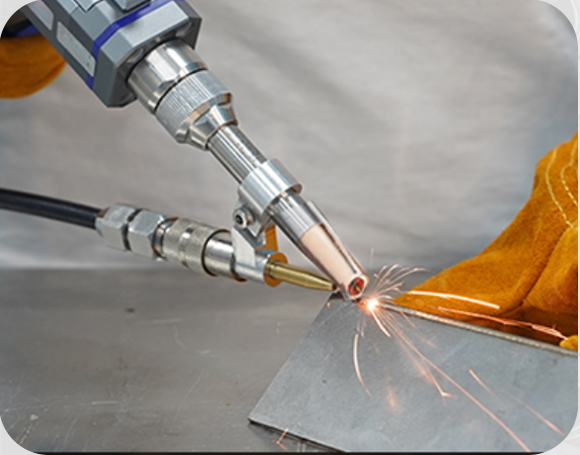
Laying the groundwork for innovation, welding technology has transformed structural fusing over a span of many years. Its history dates back to the Bronze Age when small gold boxes were made using an identical welding procedure. However, with the advancement, in current times the welding industry market value has now reached over $23 billion.
Laser welding is the most modern approach to welding techniques in this age and time. Utilizing various high-powered lasers and focusing tools drives the functional aspects of a laser welder. In the next generations, the demand for air-cooled laser welders is anticipated to outpace that of water-cooled models. This is owing to the widespread need for compact and lightweight welding equipment across multiple industry sectors.
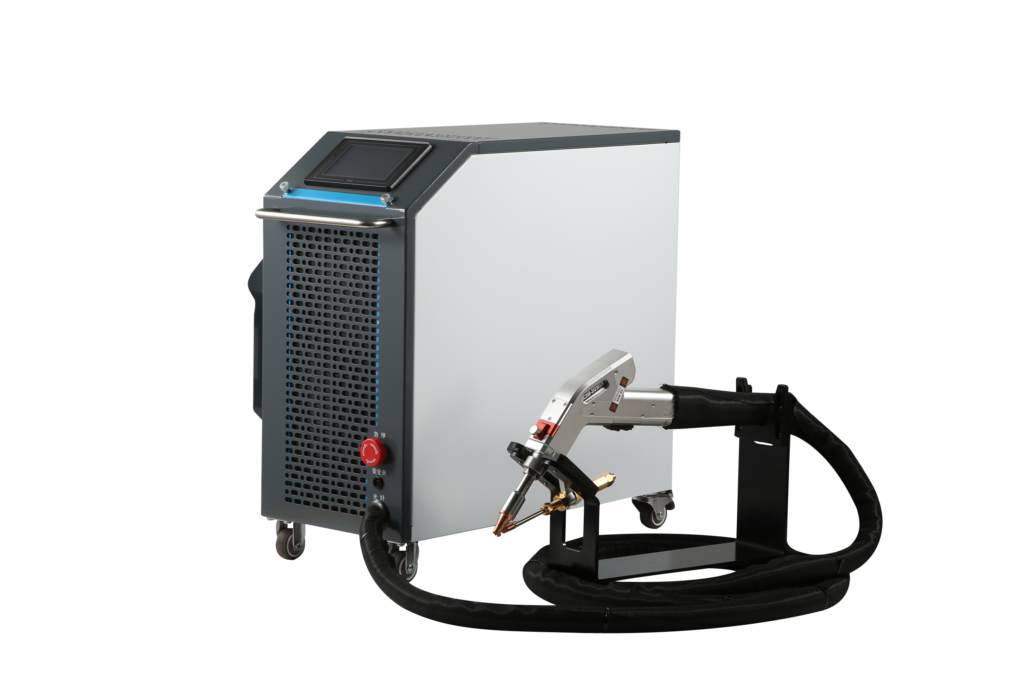
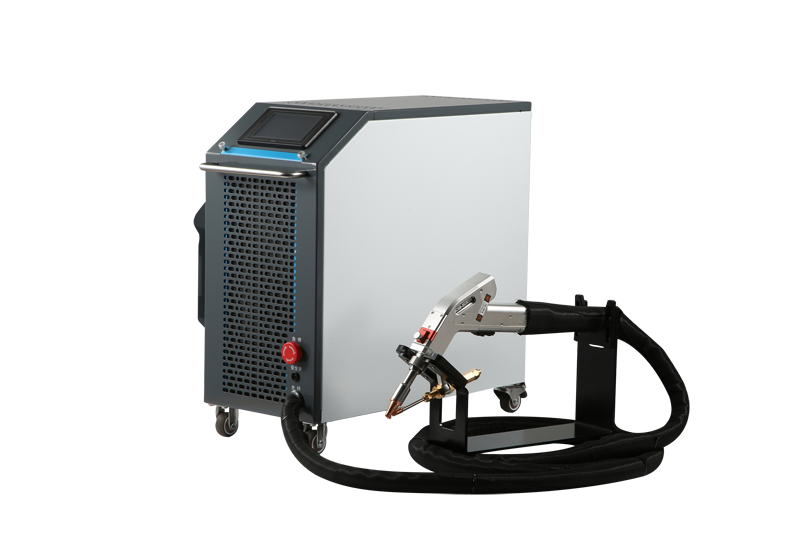
One such air-cooled laser welder that we suggest is the ComWelder which is highly affordable yet offers high-quality results. Power levels vary between 800 and 1200 watts between its B1 and B2 models. These use less electricity than alternatives since they are air-cooled. It’s a versatile welding apparatus that may be put to use in a wide variety of settings, including the home and the workplace.
Comprehensive descriptions of the advantages and disadvantages of air-cooled and water-cooled welding methods are provided below.

Detailed Explanation of Air-Cooled Welding Technology
With a typically small structure, air-cooled welding machines are compact yet high-functioning welding devices. They use air as a major factor to aid in welding. These also are well-suited for a wide set of applications.
Operational Principle of Air-Cooled Laser Welder
Compressed air is the fundamental component used in Air-cooled welding. All that is needed to operate is air and shielding gas within an air-cooled welding technique. The heat generated by the welding cycle needs these to disperse.
More rigid copper wiring is used in this. Because of this, the wire can carry power to the gun despite becoming too hot due to the intrinsic resistance of the wires.
The ComWelder B1 and B2 work on this principle and have unique air-cooled designs. These are effective tools employed in a diverse range of industries. This device has variants with two power outputs of 800W and 1200W respectively to cut stainless steel, carbon steel aluminum, etc. effectively.
The device overall is portable, weighing just below 38kg. With its compact design, users can easily take it anywhere on job sites or use it for home improvement projects without leaving any welding marks.
Physical Basis
The physical basis of air-cooled welding follows:
- The laser source generates a high-powered beam. This is then focused on the welding area by the optical focal lens used.
- The heat source typically generated by the laser beam helps in melting the parent as well as the filler metal.
- To prevent cracking and warping in the heat-focused zone, compressed air is now applied to the heated area.
- This allows the two parts of metal to fuse together and keep them in place. After this, it is left to cool so that it stays in the required shape without deformation.
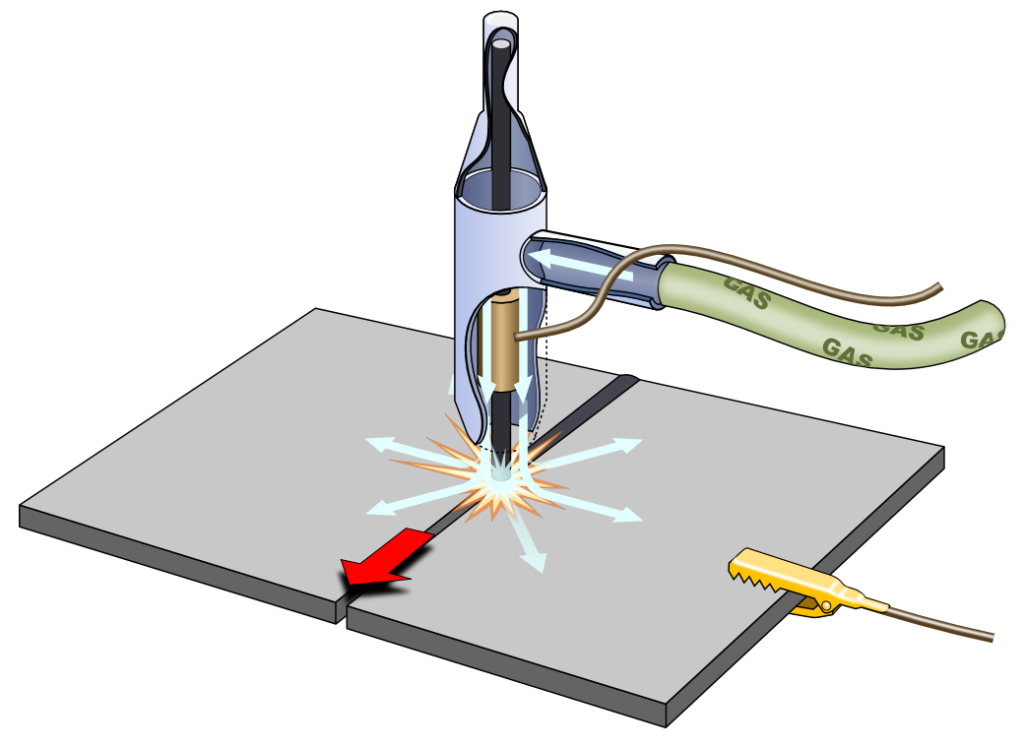
Equipment Structure and Key Components
To better understand the structure and components of an air-cooled laser welder, we have described its prominent parts below.
- The laser source – this is the major component of the machine. It generates the laser beam that moves the whole process forward.
- The welding head – It holds the laser source. It is interconnected with the scanner and the optical lens. It helps focus the laser beam on the respective area.
- The scanner – It can be either galvanometer-related or mechanical. It helps move the laser beam over the welded area.
- The cooling system – This applies air compression. It also helps the laser from heating up unnecessarily.
- Control center – Laser power, speed, density, and output are all set by this. It manages all operations.
Pros
- This device is simple to use. It is easy to set up and assemble.
- Air-cooled laser welders are inexpensive and are ideal for SMEs for volume production.
- These are high-speed devices, eligible for fast working.
- It is a versatile welder as it finds applications in a number of industries including automotive and manufacturing.
- This is lightweight because compressed air replaces the water coolant. It is highly portable, and usable in many areas.
- Another benefit of this device is that it can easily work on low energy. ComWelder B1 can easily operate on a household power socket of 220V/110V. This is also eco-friendly as there is no excess energy wastage.
- There is no need to replace the coolant of for an air-cooled welder. This makes it easy and convenient to use.
Cons
- Due to long hours of continuous working, there can be potential heat build-up. This can malfunction the drive easily If the heat isn’t dissipated correctly.
- If a fan with a strong airflow is used in this welder, it can create some noise, which can be a handicap
Detailed Explanation of Water-Cooled Welding Technology
A powerful and high-stress enduring technique that employs water as a cooling aid in welding is the water-cooled welding technology. The welding machine used for this purpose is heavy yet can create the desired results with no material oxidation. It has a distinct range of applications in several commercial sectors.
Operational Principle of Water-Cooled Laser Welder
A water-cooled welding technology draws a coolant liquid via a pump that is situated in a radiator. This is often included in or close to the power supply. It is gathered in the handle through cooling pipes in the power cord. The cooling fluid circulates back to the radiator. Here, the coolant’s heat captured is dissipated via the radiator’s deflecting process. Additionally, the surrounding air and shielding gas help to distribute the radiation from the electrical arc.
Physical Basis
The physical basis of a water-cooled system follows:
- Due to its excellent specific heat capacity, water serves as an effective cooling fluid.
- The cooling system is the core part to cool the laser source.
- A pump constantly moves water within the cover.
- It takes up the laser’s surplus heat and releases it slowly.
- After the cooling process, the water is pumped back into the system.
Pros
- A water-cooled laser welder is highly used in many industrial applications due to its rapid cooling mechanism.
- This also creates pristine and precise welds as there is no excessive buildup due to the water.
- The machine is considered highly stable as the coolant allows it to cool down rather immediately.
- This tool generally has a high durability with a lifespan of about 5 years. Its components last longer than those of other laser welders.
Cons
- A disadvantage that this welder holds is that it’s expensive to buy.
- Alongside that, it has high operating costs.
- The coolant needs replacement after some time and the equipment requires cleaning. Due to having high maintenance, it is not ideal for use.
- Water-cooled machines are heavy to move around, which decreases their convenience.
- These have an excessive overall power consumption as a result of the significant electrical usage of the water-cooling system. This means that the total power consumption is considerable and is not eco-friendly.
The Similarities and Differences Between Water-Cooled Welding Machine and Air-Cooled Welding Machine

With the industry standards, both air-cooled and water-cooled laser welding are utilized in various sectors. To understand the technical comparison of both, the subsequent information is compiled from multiple sources. These involve product descriptions provided by producers, studies from relevant industries, and feedback from users.
Similarities
1. Welding Speed
The welding speed of air-cooled laser welders is high. It can be 20-100mm/sec and can weld bulk products within a span of some time. ComWelder B1 can weld up to 10 inches per minute, which is excellent for manufacturing industries.
Water-cooled laser welders also have a high welding speed, which is 10 inches per minute.
2. Welding Quality
Exceptional welds may be created with either an air-cooled or water-cooled laser welder. These are widely recognized as reliable and capable of effective workability.
3. Range of Materials
Air-cooled welder has the capacity to weld all metals ranging from stainless steel to copper. Its range makes it a favorable tool to be used in several sectors. ComWelder B2 is ideal in this regard. Water-cooled welders are similar to this and can help fuse an extensive array of substances which include metals, plastics, etc. This makes both of these options ideal in terms of material range.
Differences
1. Heat Dissipation
Air-cooled laser welders have high heat dissipation because of the compressed air applied to the welded area. Water-cooled welders on the other hand have higher heat dissipation because of water-focused cooling ability.
2. Portability
Due to the water-filled system, water-cooled welders are heavy. This makes them not ideal for site-focused jobs. However, air-cooled laser welders use air as a coolant, which makes the equipment really light. This makes them portable and convenient for use. ComWelder B1 and B2 are lighter, weighing only 38kgs, which makes them convenient.
3. Cost
The air-cooled laser welders have low initial costs as well as low maintenance and repair costs as per industry data. Water-cooled laser welders are expensive. Their maintenance is required regularly, which is particularly expensive.
Statistical study demonstrates that air-cooled laser welders have several benefits over water-cooled ones. They provide quality welds, cost less, and demand less upkeep. Air-cooled laser welders are suitable for high-speed, superior welding. A compact, inexpensive air-cooled laser welder is an appropriate choice.

Experimental Design and Methods
For experimental purposes, a controlled material for welding is used. Two samples of materials are taken. One is welded with an air-cooled laser welder and the other with a water-cooled laser welder. A measuring device along with a computer is used to analyze the data. Use the same setting for each welding device under the same conditions. The data drawn from the experiment can depend on the upper measures and the results gathered.
Fields of Application and Case Studies
Along with various features, there is a range of applications for both devices.
Typical Applications of Air-cooled Welding
1. Thin Material Welding
Air-cooled laser welders specialize in welding thin and delicate materials efficiently. Sheet metal is used in this regard. Their heat is focused and limited, reducing the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and preventing the material from burning.
2. Inexpensive Material Welding
These are employed by SMEs and hobbyists generally. They are used to welding cheap material with less wastage. Mild steel and aluminum are ideal for this. ComWelder B1, accordingly, can weld a variety of materials rapidly with low power consumption.
3. Limited Area Welding
The areas that are difficult to reach such as car parts, engines, and internal elements of a machine can be welded using air-cooled welders. These are great to get to confined spaces and weld any parts or joints effectively.
4. Active Welding
For on-site welding, air-cooled welders are excellent due to being light. These can be easily carried anywhere for repairs, maintenance work, and other tasks.
Typical Applications of Water-cooled Welding
1. High-Stress Welding
Water-cooled laser welders are ideal for continuous work constructing and joining high-stress parts. Beams and pressure vessels can be welded easily using this. These are prone to ensure high stress levels for which such devices are utilized.
2. Thick Material Welding
Metal pipes and steels can easily be fused using water-cooled welders. Thick sheets of metal and other materials are hard to melt, and this device’s welding depth helps in this regard.
3. Environment-Resistant Welding
These are built in such a way that they are resistant to environmental elements. These can thus be used in harsh outdoor places and damp job sites.
Case Analysis and Experience Sharing
Case examples and insights gained from using both air-cooled and water-cooled laser welding are provided below.
Case Study:
Thin-material welding using an air-cooled laser welder
Medical device manufacturers often employ air-cooled laser welders for joining thin components like sheet metal. Laser welders that use air cooling may safely join fragile components without melting or distorting them. Due to the critical nature of producing reliable and efficient medical equipment, this is crucial for the business.
Experience Sharing:
The portability of air-cooled laser welders is an advantage.
One worker described their experience utilizing portable, air-cooled laser welders. These are reportedly easy to carry about. They were able to weld in inaccessible areas since they are portable. According to the report, the cost of air-cooled laser welders is much lower than that of water-cooled models. Because of this, they were an appropriate choice for them.
Selection and Decision Factors
After discussing all details along with variable features, the final selection and decision-making require investigation. Consideration of a few factors between air-cooled and water-cooled laser welding is required, as elaborated below.
Investment and Operating Cost Analysis
According to the data, the initial investment cost of air-cooled laser welders is similar to water-cooled welders. On the other hand, the price of maintenance varies widely between the two. When power costs are included in, the difference of expenses increases even further. When compared to a water-cooled welder , an air-cooled welder uses 50% less energy. The annual savings for this are $2,000.
Technical Adaptability and Future Scalability
Air-cooled and water-cooled laser welders alike may be modified to work with innovative technologies and methods. Welding heavy materials or those that demand a lot of energy might be more appropriate for water-cooled laser welding. When accessibility or finances are paramount, air-cooled laser welders can be the best option.
The demands of mass manufacturing and future scalability may be met through air-cooled and water-cooled laser welders. But water-cooled laser welders can be superior in strength and endurance for this purpose. With their lower price tag and greater portability, air-cooled laser welders might be ideal for midsize factories.
Safety, Environmental Considerations, and Regulatory Compliance
The intense heat from air-cooled laser welders may burn skin and clothes. Fumes from them may be dangerous when inhaled. Vaporized water is the byproduct of water-cooled laser welders. Water vapor may burn flesh and clothes as well. Inhaling it in high amounts is likewise dangerous.
All the water used in operating an air-cooled laser welder is recycled, and the machines use less electrical energy overall. Excess water from water-cooled laser welders has to be handled appropriately.
Future Trends and Technological Developments
Laser welding technology and consumer demand are linked. Investing in revolutionary development arises with laser welding needs to extend with respect to future trends. Research has produced stronger, more accurate, and adaptable laser welders.
- To meet the requirement for welding thin substances, air-cooled laser welders were developed. The need for welding bulky components has given rise to water-cooled laser welders.
- Powerful and precision-oriented lasers enable laser welders to join more dense, higher-reflectivity, and complex-geometry substances.
- Efficient and eco-friendly laser welders expand laser welding into emerging sectors.
- These tendencies suggest that laser welding will continue to advance. This will eventually become a flexible and productive welding method.
- Future innovations include fiber lasers. As novel welding methods are created, laser welders may be utilized to attach a greater variety of components and materials.
- The development of innovative software simplifies the process of setting up and operating laser welders.
Concluding Note
Laser welding has been in the manufacturing and maintenance industries for several years. Air-cooled and water-cooled laser welders have seen tremendous usage in varying industries due to their flexible welding nature. However, due to overall welding speed, quality, range of materials, cost, and applications in industry air-cooled laser welding is the preferred choice.
ComWelder B1 with its high power output and high precision with low maintenance cost can be an ideal option. We hope this article elaborates on all the details regarding the major advantages and disadvantages of air-cooled laser welding and water-cooled laser welding effectively.