Building and maintaining metal structures requires the application of welding. Strong and permanent joints for metal structures are made possible by fusing the parts together. In this regard, manufacturing processes readily require the use of efficient welding equipment to streamline the process.
Whether in SMEs or large-scale industries, welding tools play an integral role in constructing, assembling, or repairing metal-related parts. The tool manufacturing industry, automotive sector, construction industry, energy infrastructure industry as well and home improvement areas have benefitted from welding for years.
Starting from the Bronze Age, welding techniques have been the oldest repairing and production technologies industry-wise. The oldest techniques dating back from melting metal to modern gas and arc welding in the 19th Century define its evolution over time.
The 20th and 21st Centuries further played a role in the development of welding strategies. This is with the introduction of Robotic and Laser welding. With time these have made the entire procedure precise and fast with minimum error or damage. From metal works in buildings, and bridges to aircraft and cars, complex and simple structures are made possible with the modern laser welders now.
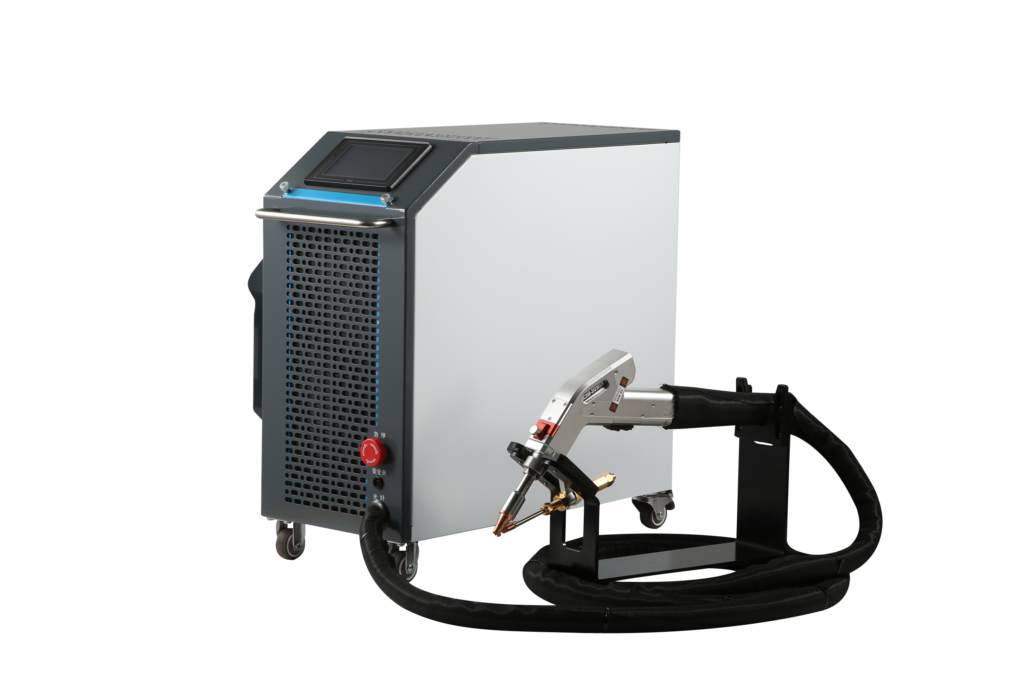
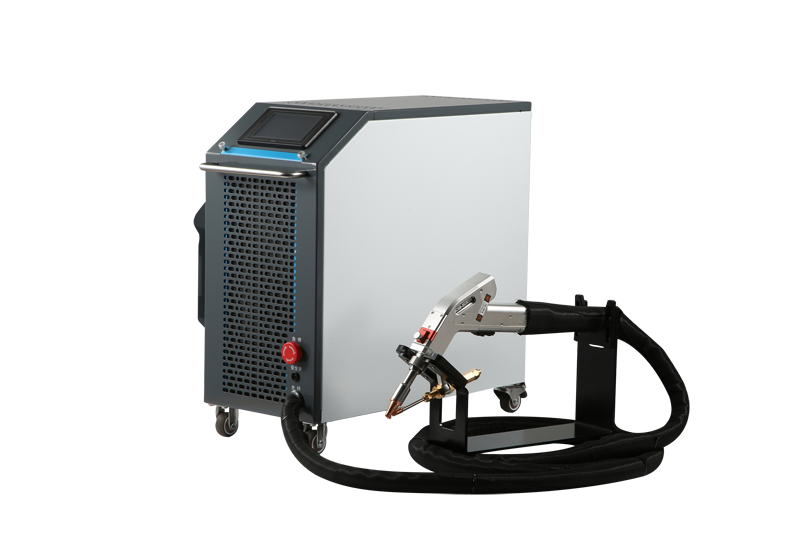
One of the affordable as well as portable laser welding options that we recommend is the ComWelder which is lightweight and effective. It comes in 2 variants, the B1 with B2, with a power range of 800W and 1200W. These have an air-cooled design and consume less power than other comparable products. This is a multipurpose welding tool and can be utilized for the majority of domestic as well as industry-related work.
In order to better understand how normal welding differentiates from traditional welding, we have outlined all the details in our article below.

Understanding the Basics
To gain an in-depth idea about how welding techniques are distinct in their own manner, we need to first understand the fundamentals regarding them.

1. Normal Welding
In traditional, normal welding, the heat directly generated from an electric current is utilized to fuse two parts of metal together. It depends on a number of factors, such as the material and thickness of the metal and the type of welding required. Its major working principle includes the fusion of base metal and filler metal. It requires cooling to avoid cracks. Although it’s reliable and safe, normal welding is definitely a time-consuming process and there are other modern methods and equipment available.
Common Types of Normal Welding
Normal welding is not considered just one method. It consists of many different types of welding processes utilized. Some of these are mentioned below.
(1). Arc Welding
The first type is arc welding, which utilizes an electric arc. The heat from the arc is concentrated on the heating zone to connect the two metals together.
- This is further divided into Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW).
- This is a versatile process and welds metals of varying thicknesses and positions.
- Fume and time consumption are two main flaws of this process.
(2). MIG
This kind of welding may be fully or partially automated. A barrier gas and electrode wire are constantly delivered into the device. This causes an arc to form. This melts the parent metal and the filler material.
- Most often, steel or copper cables are used as the electrodes.
- Argon and CO₂are often used as shielding gases.
- It is highly economical.
- Sheet-metal welding, home improvement, and the automotive industry generally used this.
(3). TIG
This is a kind of manually operated welding. To generate an arc, it employs an operational tungsten electrode and an insulating gas. The arc then liquefies the filler metal and the main metal.
- Usually, argon or helium is used as the gas for shielding.
- This is generally time-consuming.
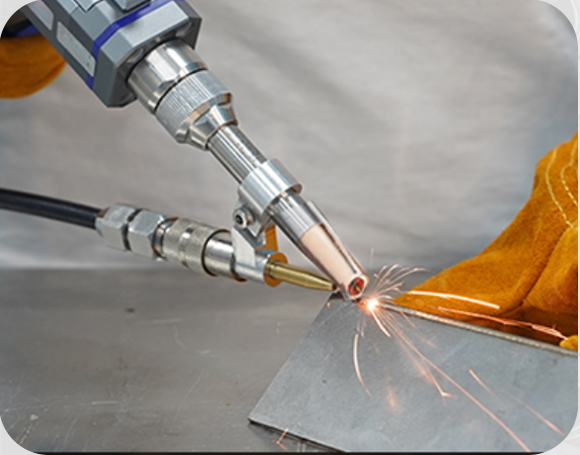
2. Laser Welding
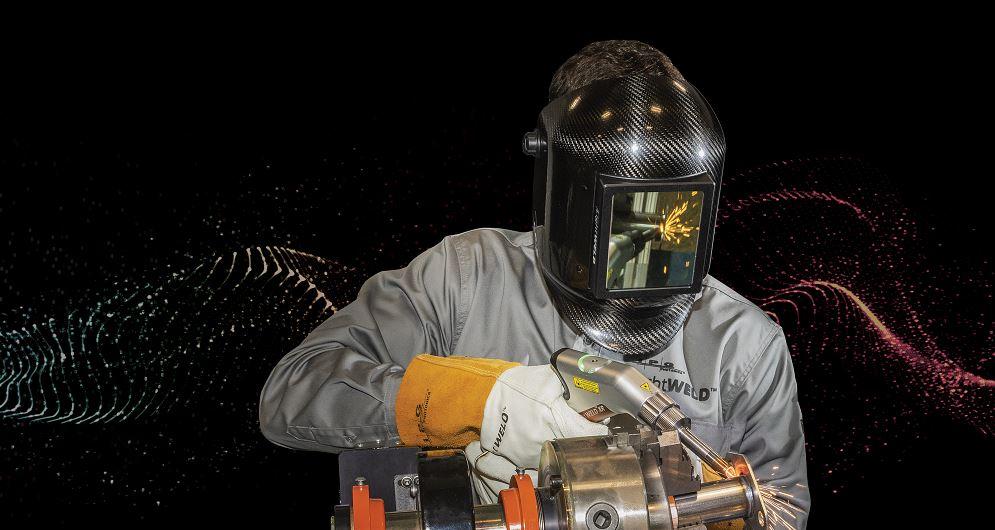

The second, more advanced and effective sort of welding is Laser-oriented. It is primarily based on utilizing a laser beam source for heat. This heat is focused on the welded area between the parents and filler metals. High-volume production is facilitated through this type of welding.
- Its penetration and strength ability are comparatively much higher than normal welding. ComWelder B1 is an ideal example of this, with a welding depth of/8th inch for a 16-gauge steel.
- For delicate and complex metal parts, laser welding is excellent as it does not damage the material. Its precision makes it highly sought after, such as ComWelder B1 welds with a precision of +/- 0.005 inches.
- Little to no fumes are generated through laser welding, making it a safe and eco-friendly process.
Key Distinctions Between Normal and Laser Welding
Laser welding is generally more in demand these days among SMEs because of its accuracy, efficiency, and portable nature. To further elaborate on the prominent differences between laser welding in relevance to normal welding, we have discussed a few points further.
(1). Precision and Control
Due to being focused on a specific point, laser welding can be highly precise. There is no element of heating distortion in this, which makes it more concentrated. Laser welding is also automatically operated, making it easy to handle with no human error involved. The ComWelder is a powerful tool in this regard, as it shows high precision and welding ability.
Normal welding on the other hand has low-medium precision, making it less functional. It generally only works on thicker materials. The electric arc used in normal welding is not as concentrated. It also causes metals to oxidize, which can weaken the jointed area.
(2). Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
Another major difference is the heat-affected zone in welding, where heat is applied, but it doesn’t melt. The HAZ is narrower in laser welding, as the laser is concentrated on a limited point. This keeps the rest of the area cool and secure from the effects of the weld. ComWelder B1 has an air-cooled heat dissipation design, which helps in this regard.
Contrarily, the HAZ is much wider in ordinary welding. This is because the melt arc is focused on a broader area, which can reach extremely high temperatures. It also depends on the kind of material welded.
(3). Speed and Efficiency
If we talk about speed, then laser welding is a pretty fast technique. Its laser beam is strong enough to melt the metal surface quickly, aiding in bulk production as well. Discussing the ComWelder in this regard, it can weld at a speed of up to 10 inches per minute, which is high. Alongside this, this has low power consumption. It can easily operate on a household socket of 220V or 110V without delays. Apart from this, laser welding consumes less material because of narrow area focus welding.
In contrast, normal welding has various methods such as TIG, which uses manual welding. It can be time-consuming, thus not ideal. Its speed is low, and it uses more material than the electric arc focus area is wider. This causes more waste, and it uses much more energy than laser welding.
(4). Material Restrictions
High-quality welds are a great end result of laser welding. It can create durable welds on materials such as stainless steel, copper, titanium, aluminum, brass, and nickel. Apart from this, it can also weld refractory metals.
Normal welding on the other side has the ability to easily weld thick materials such as steel, cast iron, bronze, tungsten, etc. It is not ideal for delicate and thin metal surfaces.
(5.) Equipment and Setup
The equipment required to run the whole laser welding process requires a laser welding machine, laser welding torch, wire feeder along safety gear. Laser welding tools are generally more complex to set, as the laser welding machine must be precisely aligned with the weld area.
When setting up, the welding specialist must also take into account a number of things. Laser beam attributes including intensity and beam mode, as well as the wavelength and energy density of the converging beam, may be controlled on a finer level. The laser beam must also be set up appropriately. ComWelder comes with all the equipment and adjustable welding width.
Ordinary Welding equipment is way less complex as the electric arc is created in an automatic way. The setup time is way less complicated even though the operation is difficult.
Applications and Industries
Ordinary welding is opted in a number of industries due to its affordability and convenience.
Construction
Within the construction industry weld beams, bars, pipes, and other parts, traditional welding is used.
Manufacturing
To weld appliances and machinery parts and accessories, normal welding is applied.
Automotive:
Frames of cars in the automotive industry and other parts effectively use traditional welding techniques such as SMAW and MIG
Shipbuilding:
Another sector where traditional welding is still used is shipbuilding. Welding hulls and decks require high heat potential, whereas normal welding is useful.
Mentioning the unique industries that have adopted laser welding are elaborated on below.
Medicine:
The medicine industry uses high-tech equipment and requires high precision. To weld surgical and other medical tools, laser welding is applied. ComWelder B2 is a portable tool in this aspect.
Aerospace:
Aircraft components within the aerospace industry seek strength in welding as well as accuracy. Aircraft wings, engines, etc. can be safely welded in place by laser welding tools.
Automotive:
The automotive sector for the latest cars requires accuracy and quality. To weld car bodies, frames, and other accessories, laser welding tools are employed.
Electronics:
Circuit boards as well as semiconductors require low heat dissipation. For the electronic industry, laser welding is ideal as it offers an air-cooled design.
3D Welding:
In the manufacturing sector, 3D objects, sculptures, and item prototypes can be made using laser welding. It requires varying positions to weld, which is a prominent feature of laser welding.
Micro welding:
Small parts require precision welding. Microelectronic and surgical implants are areas that require laser welding.
Safety Considerations
Normal welding can be a risky activity and should only be done by professionals. Some of its safety risks, hazards, and precautions for ordinary welding include the following.
- Shock hazards can be created if anyone comes in contact with the electric circuit acting as the power source. Protective equipment such as glasses, shields, and gloves should be used to avoid this.
- The electric arc can cause burns If the person comes in contact with the skin. Also, make sure there are no flammable materials in the working area of a welding tool.
- Normal welding causes more fumes, which can be dangerous for health and the environment. A ventilation system should be used in the area of the welding.
Laser welding on the other hand has a different set of risks. We have elaborated on the hazards and safety measures of laser welding below.
- Laser eye injuries, and severe skin burns, can be caused due to the high-power beam of the laser. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) such as safety-standard approved face shields, protective clothing, gloves, etc. should be used when using laser welding tools.
- Inflammable materials in the vicinity If come in contact can cause fire risks. Fire extinguishers should be kept close to eradicate this.
- Ensure that the laser welding machine follows the standards of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Future Trends and Innovations
With time, normal welding has modernized with technological advancements.
- Welding materials and components have improved with time. The welding wire materials such as flux-cored or metal-cored and welding heads have changed. More durable substances are used.
- Computerized programs are also integrated within traditional welding measures to automate the process.
- CNC welding machines are also created to evolve joint welding with precision.
Market size for laser welding worldwide, is estimated at over $1.96 billion. To revolutionize laser welding, numerous latest developments have been made in the field.
- With AI integration and robotics, the software used to operate the welded equipment can be monitored in great detail. It can further smooth out any lag that might have restricted the procedure.
- LBW efficiency improvements are made to make the laser beam more precise. This opens doors to weld complex structures without high energy consumption.
- With such innovations, laser welding tools are highly desired in a vast set of industries, mainly construction, manufacturing, and automobiles. This can lead to market saturation and cost-effective welding machines for SMEs.
- Its contactless approach is a turning point in the welding field, as it can reduce the worker’s stress and expertise level.
Conclusion
Welding has long been used as a beneficial technique to fuse metal parts together in various industries. However, laser welding differentiates from normal welding in terms of high efficiency, high speed, welding depths, handling potential, and intensity. With low fume production and energy consumption, laser welding equipment such as ComWelders are ideal for complex welding tasks. We hope this article was of maximum help to you.